The Phytosanitary Certificate (PSC) main motive is extending protection and safeguarding the consignment. Further, aids to avoid pests in consignment and thereby, conserve the biodiversity of the importing country by abiding the Sanitary and Phytosanitary Agreement (SPS). Phytosanitary certificate is compulsory for custom clearance and exporting agricultural commodities from India. In India directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine and Storage (PPQS) are in charge of issuing phytosanitary certificate. For export of agricultural commodities to USA it is necessary for the company to register with National Plant Protection organization.
Internationally, National Plant Protection organization (NPPO) inspect and certify the consignments on fulfilling the phytosanitary import requirements. Besides, it is mandatory to issue a Phytosanitary Certificate and produce the same with the shipment. Bearing in mind its validity, the PSC can be transferred via mail or any suitable electronic medium. Consequently, the obligation is applied to plants, plant products, and other specified goods that are dealt with internationally.
Note that, only a public officer authorized by NPPO or PPQS can issue the certificate for export as well as re-export. For such instances, International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPMs) available on the International Phytosanitary Portal encompasses the details and standard guidelines.
International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC),1951
To avoid the indefensible limitations that countries impose on exporters, IPPC implemented the ISPMs. Accordingly, ISPMs guides to ensure the protection of agricultural commodities. Alongside, strives to prevent the transmission of pest and diseases. The IPPC’s article V clearly states the requirement of PC and must focus on the following necessities:
- Carry out inspection monitored by officials of NPPOs or PPQS
- Attain Phytosanitary Certificate or the equivalent electronic document
Note that, any alterations without any certification is invalid. Additionally, care to issue Plant Health Certificate (PHC) only after a thorough inspection.
The Inspection
Initially, consigned goods undergo a thorough inspection. This export inspection includes sampling, laboratory testing (seeds), testing prorogation of the plant materials, visual analysis, washing tests, etc. Underscore the fact that, authorities carry out the inspection process at the exporter’s premises. Following that issue of pest-free guarantee, PSC is attainable. Prior to this, it is favorable to perform specific photo sanitation treatments to attain the sanitary requirement. Further, issue a copy of Import Permit that contains the Photosanitary requirements and treatments.
Guidelines to follow while filling the form
- Description of all the necessary things in the consignment- Name and address of the exporter, number and description of the packages, place of origin, declared means of transportation (specify the point of entry), name and type of produce, certifying statements, etc.
- Declarations- Regulated pest controls, Import permits, and Bilateral agreements
- Treatments (Dis-infestation treatment)- Name, date, type, chemicals used, Duration and temperature of the treatment
- Finally include the stamp of organization, financial liability statement, name of the official in-charge.
Procedure
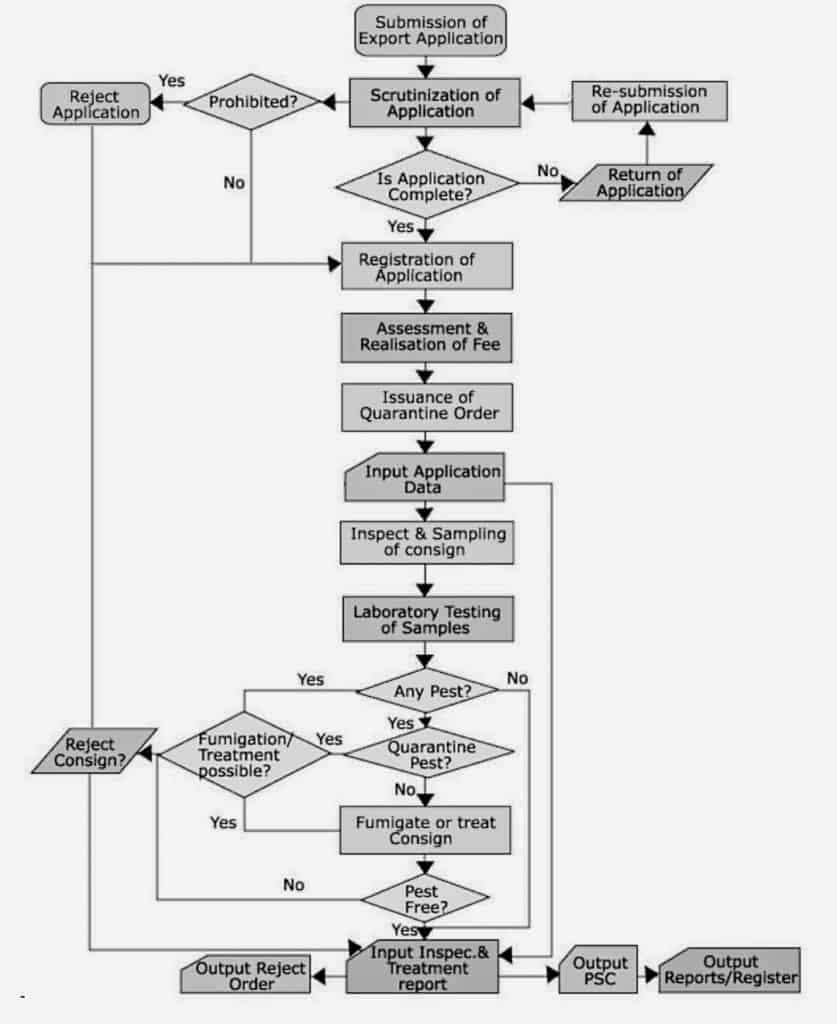
Application Registration
Filling application under Appendix-5 to the officer-in-charge is the first step to attain Phytosanitary Certificate. The time before which the application needs to be submitted varies depending on the consignment. For instance, in case of seeds consignments, the submission is 8-10 days before the shipment date. Along with the application, submit invoice copy, packing list, shipping bill, credit letter, export license, and the fumigation certificate. That apart, submit a copy of the import permit and wildlife clearance certificate (CITES). Further, the exporter should pay an inspection fee according to Appendix-2. In case the inspection is requested outside the PQ station, the extra fee must be paid before.
Inspection
Following the issue of inspection fees receipt and complete scrutiny of the application, sampling and laboratory testing commences. The officials conduct the same either at the PQ station or suitable stations at a specific time and date. That is chiefly mentioned in the quarantine order issued by the exporter. Additionally, the exporter will be in-charge of the transport and necessary facilities for opening, viewing, sampling, repacking, etc. Furthermore, the testing of seeds will follow the guideline laid in the International Seed Testing Association (ISTA). While, in case of cereals, pulses and other eatables will be under the Bureau of Indian Standards. Highlight the point that, the exporter may accompany the official in the course of the inspection to suggest their need for Phytosanitary Certificate.
Fumigation (Treatments) of the goods
In certain cases ensuing the inspection, this step is undertaken. In other words, if any kind of infestation or contamination is found during the inspection, treatment of the consignment is advised. During such instances, the exporter will prepare to fumigate the consignment at the PQ premises or another suitable place. Accordingly, the report must apply to state this purpose in Appendix-6 and subsequently pay a supervision fee of Rs 25 per container. Moreover, the exporter will bear the charges for the entire process of fumigation. Empty and stuffed container fumigation compulsory for export of agricultural goods.
Issuing the Phytosanitary Certificate
Succeeding the fumigation process, the consignments will undergo re-inspection. Consequently, after the completion of this entire process is the issue of Phytosanitary Certificate. Clarify that, the officials may issue the PSC or reject the plea accordingly. Office issues original certificate for the exporter and a copy retrieved for office archives after clearance of consignment free from pest. However, if the consignment has a live infection it is rejected, and an intimation is sent to the exporter immediately with specific reasoning. On the other hand, the re-inspected goods will apply for PSC using the format prescribed in IPPC.
Key Points to Remember
Crucial points to bear in mind during the process as ignoring minute yet specific details will lead to rejection as well as punishments
- All the pages must bear the seal, sign, date, time, and the specification emphasized by the PSC officials. Alongside add the attachments at appropriate sections.
- The certificate can be sent with the consignment or via electronic means.
- Only in extreme cases, the exporter can re-issue the PSC. Similarly, avoid alteration unless it is rigidly necessary.
- Fill the form duly with correct and complete information as an error in application leads to rejection.
- Deceitful forms such as no official sign, no date or no stamp is a punishable offense.